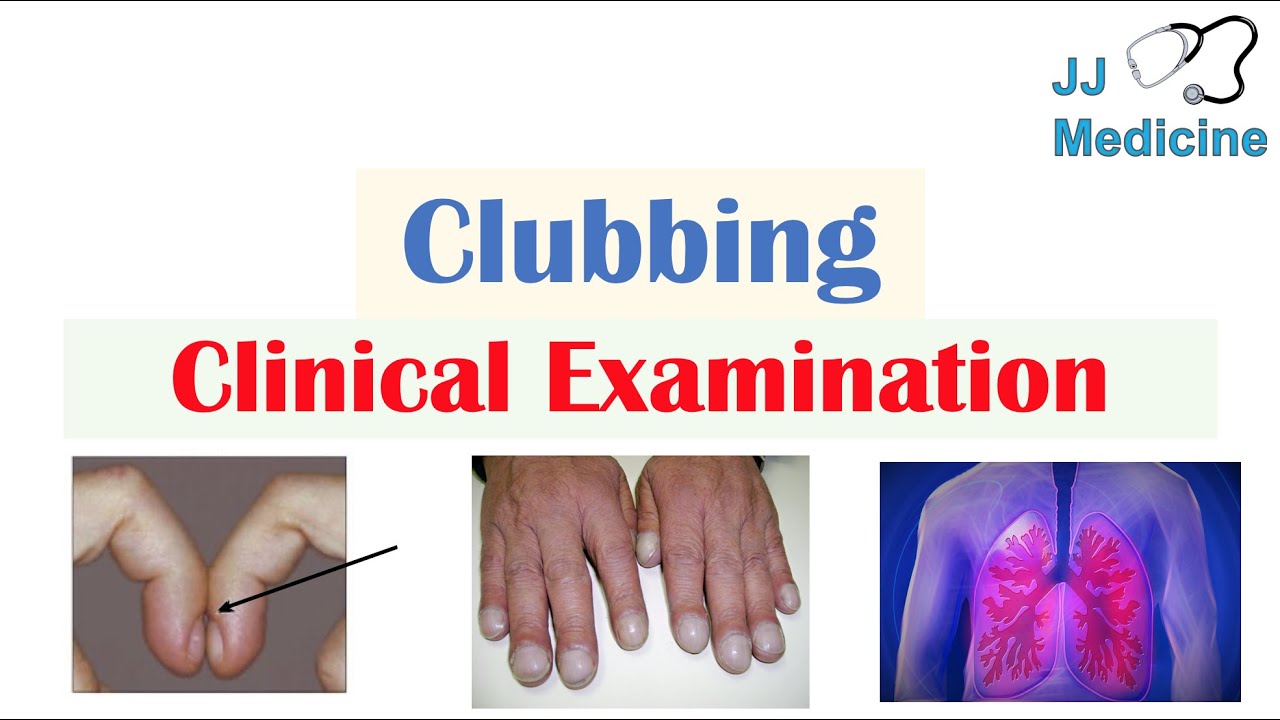
Clubitis is a rare and intriguing condition that often goes unnoticed due to its subtle manifestation of symptoms. For those who might be unfamiliar, clubitis primarily affects the fingers and toes, leading to changes that can be both visually striking and medically significant. Understanding these symptoms through pictures can provide a clearer insight into the condition, helping individuals recognize early signs and seek appropriate medical guidance.
The term "clubitis" stems from the characteristic clubbing of the fingers and toes, a condition that alters the normal shape and structure of these extremities. While clubitis itself may not be life-threatening, it can be indicative of underlying health issues, such as cardiovascular or pulmonary diseases. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms through detailed images is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
In this extensive guide, we'll delve into the visual aspects of clubitis disease symptoms, providing a comprehensive overview of what to look for and how these changes can impact one's health. Through a series of detailed headings and subheadings, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, ensuring a thorough understanding of this unique condition.
Table of Contents
- What is Clubitis?
- Causes of Clubitis
- Early Symptoms Pictures
- What are Progressive Symptoms?
- How is Clubitis Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Clubitis
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Symptoms
- Impact on Daily Life
- Can Clubitis be Prevented?
- Related Health Conditions
- Case Studies and Real-life Examples
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Clubitis?
Clubitis, also known as digital clubbing, is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of the fingers or toes, often resulting in a bulbous appearance. This condition occurs when the tissue under the nail bed thickens, leading to a change in the angle at which the nails grow. Clubitis is often indicative of underlying systemic diseases, such as heart or lung disorders, although it can also occur as a standalone condition.
The pathophysiology of clubitis is not entirely understood, but it is believed to involve increased blood flow to the affected areas, possibly due to vascular changes or chronic hypoxia. The condition can be congenital or acquired, with the latter often associated with chronic illnesses. Clubitis is more than a cosmetic issue; it serves as an important clinical sign that may warrant further medical investigation.
Causes of Clubitis
Understanding the causes of clubitis is essential for diagnosing and managing the condition effectively. Several factors can contribute to the development of clubitis, including:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Conditions such as congenital heart defects or endocarditis can lead to clubbing of the fingers and toes.
- Respiratory Disorders: Chronic lung diseases, including cystic fibrosis, emphysema, and lung cancer, are common culprits.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Liver cirrhosis and inflammatory bowel disease may also be associated with clubitis.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be predisposed to clubbing due to hereditary factors.
- Idiopathic Causes: In some cases, the cause of clubitis remains unknown, and it may occur independently of other health conditions.
Early Symptoms Pictures
Identifying clubitis in its early stages can be challenging, but pictures can serve as a valuable tool for recognizing initial symptoms. Early signs of clubitis may include subtle swelling and softening of the nail beds. These changes are often accompanied by a loss of the usual angle between the nail and the cuticle.
Pictures of early-stage clubitis typically show a gradual widening of the fingers or toes, with the nails appearing more rounded than usual. This rounding effect can be further accentuated by the increased curvature of the nail, leading to a distinct appearance that is often described as "drumstick" fingers or toes.

What are Progressive Symptoms?
As clubitis progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and easier to identify. Progressive symptoms include:
- Increased Curvature of Nails: The nails may become more convex, curving over the fingertips.
- Enlargement of Fingertips: The tips of the fingers or toes may swell, creating a bulbous appearance.
- Thickening of Nail Beds: The tissue beneath the nails becomes thicker, contributing to the change in shape.
- Loss of Nail Angle: The angle between the nail and the cuticle becomes almost nonexistent.
Progressive clubitis is often accompanied by more severe underlying conditions, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical attention if these symptoms are observed.

How is Clubitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing clubitis involves a combination of physical examination and medical history analysis. Healthcare professionals typically look for:
- Physical Examination: Observing the shape and structure of the nails and fingertips.
- Medical History: Reviewing past and present health conditions that may contribute to clubitis.
- Diagnostic Tests: In some cases, imaging studies or blood tests may be conducted to identify underlying causes.
- Specialist Referrals: Referral to specialists such as cardiologists or pulmonologists for further evaluation.
Accurate diagnosis is key to managing clubitis effectively, as it often signals other health issues that require attention.
Treatment Options for Clubitis
Treating clubitis involves addressing the underlying causes rather than the symptoms themselves. Common treatment strategies include:
- Medical Management: Treating the primary condition, such as heart or lung disease, often resolves the clubbing.
- Medications: Prescribing drugs to manage symptoms or underlying conditions, such as anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive agents.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for severe conditions contributing to clubitis.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing assessment by healthcare professionals to track changes in symptoms and adjust treatment as needed.
Effective management of clubitis relies on a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical manifestations and the underlying health issues.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Symptoms
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing clubitis symptoms. Recommended changes include:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity to improve cardiovascular and respiratory health.
- Avoiding Smoking: Eliminating tobacco use to prevent exacerbation of symptoms and underlying conditions.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques to reduce stress and its impact on health.
These lifestyle modifications can enhance the effectiveness of medical treatments and promote better health outcomes for individuals with clubitis.
Impact on Daily Life
Clubitis can have varying effects on an individual's daily life, depending on the severity of the symptoms and underlying conditions. The changes in the appearance of the fingers and toes may lead to self-consciousness or discomfort. Additionally, if clubitis is associated with chronic health issues, it may impact physical activities and quality of life.
Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential for managing the emotional and physical challenges posed by clubitis. Awareness and education about the condition can also help reduce stigma and improve acceptance.
Can Clubitis be Prevented?
While it may not always be possible to prevent clubitis, particularly in cases with a genetic predisposition, certain strategies can minimize the risk of developing the condition:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Routine medical examinations can help detect and manage underlying conditions early.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: Reducing exposure to factors that contribute to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, such as smoking.
- Early Intervention: Seeking prompt medical care for symptoms associated with heart or lung problems.
These preventive measures can support overall health and reduce the likelihood of developing clubitis.
Related Health Conditions
Clubitis is often associated with a range of health conditions, highlighting its role as a clinical marker. These conditions include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A group of lung conditions that obstruct airflow and are linked to clubbing.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic disorder affecting the lungs and digestive system, often presenting with clubbing.
- Congenital Heart Disease: Structural heart defects present from birth that may cause clubbing.
- Liver Cirrhosis: A chronic liver disease that can lead to clubbing due to impaired liver function.
Recognizing the connection between clubitis and these conditions is crucial for holistic patient care and treatment.
Case Studies and Real-life Examples
Examining real-life examples of individuals with clubitis can provide valuable insights into the condition and its management. Case studies often highlight the diverse presentations of clubitis and the importance of personalized care strategies.
For instance, a young adult with congenital heart disease may exhibit clubbing as a primary symptom, prompting early intervention and surgical treatment. In another case, an older adult with chronic lung disease might develop clubbing gradually, necessitating ongoing respiratory therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
These examples underscore the need for a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment, considering each patient's unique medical history and health needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes clubitis?
Clubitis is often caused by underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular or respiratory diseases. It can also occur due to genetic factors or remain idiopathic in some cases.
Can clubitis be reversed?
While clubitis symptoms may improve with treatment of the underlying condition, complete reversal is not always possible. Early intervention and management are key to improving outcomes.
Is clubitis painful?
Clubitis is typically not painful, but the associated conditions may cause discomfort or pain. Addressing the root cause can help alleviate any pain experienced.
How common is clubitis?
Clubitis is relatively uncommon and often associated with specific health conditions. Its prevalence varies based on the underlying causes and population demographics.
What specialists treat clubitis?
Treatment of clubitis may involve specialists such as cardiologists, pulmonologists, or gastroenterologists, depending on the underlying condition.
Are there any home remedies for clubitis?
While home remedies alone cannot treat clubitis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking can support overall health and symptom management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, clubitis is a complex condition with diverse causes and manifestations. By understanding its symptoms through pictures, individuals can become more aware of potential health issues and seek timely medical intervention. A comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, coupled with lifestyle modifications, can improve the quality of life for those affected by clubitis. Through education and awareness, we can enhance recognition of this condition and its significance in the broader context of health and wellness.
Essential Insights Into Www Downloadhub Net For Movie Enthusiasts
Willard Ford: A Life Of Creativity, Innovation, And Influence
Intriguing Aspects Of Drake Dick Photo: A Comprehensive Examination